In server monitoring service we have come across the term Process many times and we are here explaining what is mean by a process in Linux systems
Program Vs Process
- A program is an executable file, while a process is a program in execution. A program is a set of instructions written down to do something, while a process is the result of executing a program.
- Process Vs Thread
A process and a thread is almost the same, and the only worthwhile difference between a thread and a process is that threads share the same address space completely and hence require less creation time. Processes are independent execution units that contain their own state information, use their own address spaces, and only interact with each other via inter-process communication mechanisms. A thread is a coding construct that doesn’t affect the architecture of an application. A single process might contains multiple threads; all threads within a process share the same state and same memory space, and can communicate with each other directly, because they share the same variables.
- User process is a process run by a human user
- A service or a daemon process which can be time based or event based usually triggered by root or the system itself while on bootup and infact a never ending process which triggers other processes.
- PID – Process ID – The id of a process, each process running on a system is assigned itś own process ID.
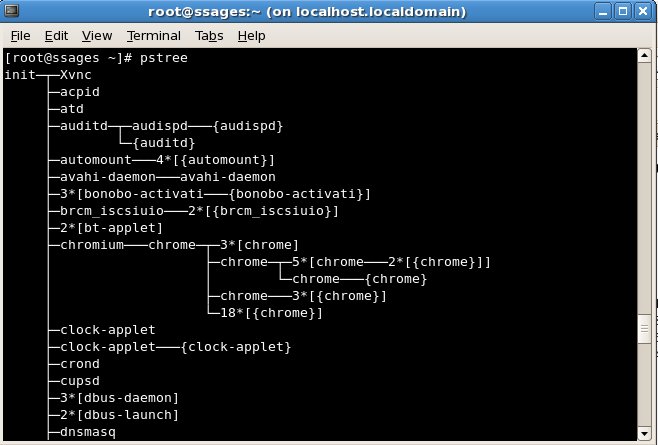
- PPID – Parent Process ID – PID of the process that created the child process. pstree shows the relation b/w parent process and other process, starting from init.
- Job ID – Job ID is unique to a shell instance. Can be displayed using the command “jobs”. A process when hit a “Ctrl+Z” shows the job id, when it says Stopped .The command jobs shows background processes, both stopped and running. The process having a + symbol toward the right of job id means that process will be responding to fg without options (without job id being passed as argument) and the – sign to any process, if any indicates that it is that process which inherits the + sign after the process having + sign is done with.
- bg %job_id or bg PID will let the process with job_id to run again.
A few process related commands with options:
ps command (process status) will display snapshot information of all active processes.
To display all the processes running in the system
Use “ps aux”, as shown below.
You can also use “ps -ef | more”, to get a similar output
Use ¨pstree¨ to get output like this:
- Nice Value:It is used to run a program with modified scheduling priority . Nicenesses range from -20 (most favorable scheduling) to 19 (least favorable). Nice is to start a process with a priority like nice -n 10 mp3blaster
- Renice – renice is to change the priority of an existing process like : renice 10 PID
- kill – terminate a process
The command kill sends the specified signal to the specified process or process group. If no signal is specified, the TERM signal is sent. - kill – kill %job_id or kill PID / man 7 signal
- kill -15 PID – cleaner or soft killing of process – SIGTERM
- kill -9 PID – hard kill – SIGKILL
- kill -19 PID – Stop the process – STOP
- kill -18 PID – resume the stopped process – SIGCONT
- kill -2 PID – equivalent to Ctrl + C – SIGINT
- kill -1 PID – Hangup – SIGHUP
- kill -3 PID – end process & core dump
- killall
More information regarding ‘kill’ can be found at the man page
[root@localhost ~]# man kill
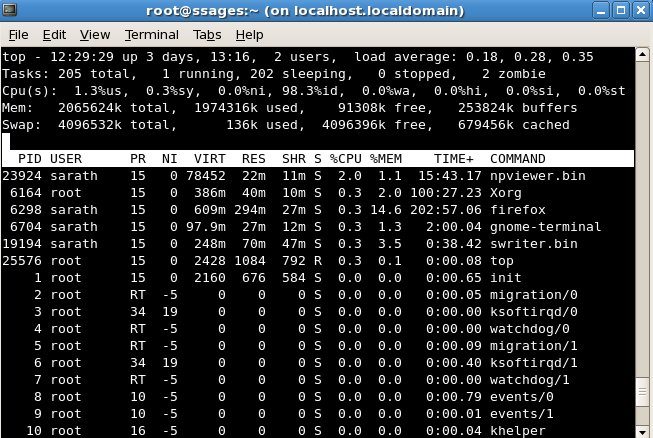
Top – Display Linux tasks
The top program provides a dynamic real-time view of a running system. It can display system summary information as well as a list of tasks currently being managed by the Linux kernel.
top – Sort by CPU -> P
Sort by MEM -> M
Sort by PID -> N
Kill by PID -> k
Renice by PID -> r
List by user -> u
Active processes or non idle process -> i
- nohup – will stop a process from being killed even if you logs off the system before it completes. It ignores the hangup and quit signals.
- pgrep – process grep.
pgrep looks through the currently running processes and lists the process IDs which matches the selection criteria to stdout. All the criteria have to match.
For example, pgrep -u root sshd
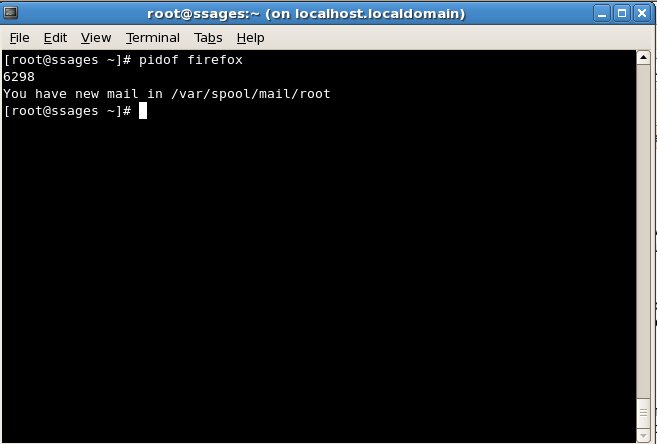
- pidof – find the process ID of a running program. finds the process id’s (pids) of the named programs. It prints those id’s on the standard output. An example is given below
- PPID – Parent Process ID
The process parent PID, the creator of the process.
- STAT – Process Status
These functions return information about the specified file. You do not need any access right to the file to get this information but you need search rights to all directories named in the path to the file.
TTY – Controlling Terminal
It print the file name of the terminal connected to standard input .
[root@localhost ~]# tty
/dev/pts/5
- PRI – Priority number.
Lower the number, higher the priority, from +19 to -20. The priority numbers available for the system is from +39 to -60, while -20 to -60 is reserved for kernel threads. A normal user can have priorities from 0 to +20, and negative values as well as reducing the values are allowed only to root.
NI – Dynamic priority value , ranges from +19 to -20
TIME – total CPU time used
Process Status (STAT) Codes can be of any of these.
D uninterruptible sleep (usually IO) – cannot be terminated at the moment.
R runnable (on run queue) – can be run
S sleeping – waiting for an external event
T traced or stopped – is suspended.
Z a defunct (“zombie”) process – has terminated itself.
X Extinct – is dead
Setting limits on the number of processes that can run.
The command “ulimit” is used to limit the number of processes users can run along with available system resources. All processes which will be started from the shell (bash in many cases), will have the same resource limits. To set the limits for daemons which are running at boot time add ulimit
command to boot scripts. See apache startup script.
/etc/security/limits.conf
For example:
[root@localhost ~]#ulimit -S -m 1000000 [root@localhost ~]# ulimit -S -v 500000
With this value set, the system will kill any process that tries to take up more resources than you have set as a limit.
For Linux server monitoring service, do contact our server monitoring team with your requirements