Published on: June 26, 2017 by Anitta Jose

Scenario:
A stream editor is used to perform basic text transformations on an input file. Sed command is mainly used to replace the text in a file. But it is a powerful text processing tool.
Consider the text file “test” as an example
1) Replace all the occurrence of the pattern in a line
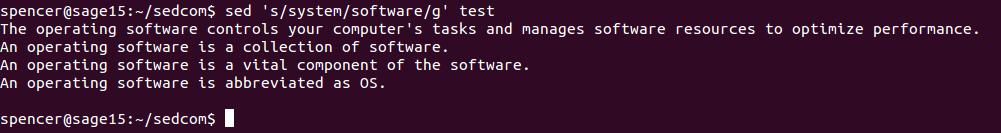
Here in the above example, sed is used to replace all occurrences of “system” with “software” within the file test.
Let us have look into the switches used for the task
| Denotes | |
| s | Substitution operation |
| / | Delimiter |
| system | Search pattern |
| software | Replacement string |
| g | Global Replacement flag |
Sed command by default replace only the first occurrence of a string in each line. The /g flag specifies the sed command to replace all the occurrences of the pattern in each line.
The table below shows some more options:
| Command | Purpose |
| sed ‘s/system/software/’ test | Replace first occurrence of a string in each line |
| sed ‘s/system/software/n’ test | Replace the nth occurrence of a pattern in a line |
| sed ‘s/system/software/ng’ test | Replace from nth occurrence to all occurrences in a line |
| sed ‘n s/system/software/’ test | Replace string on a specific line number (nth line) |
| sed ‘n,$ s/system/software/’ test | Replace string on a range of lines (from nth line till last) |
| sed ‘/as/ s/system/software/’ test | Replace on a line which matches a pattern (here pattern is “as”) |
| sed ‘s/system/software/w test2’ test | Copy replaced line to another file |
| sed ‘/your/ c Replaced line’ test | Replace the lines which contains a pattern (In this case, the entire line with the pattern “your” will be replced with “Replaced line”.) |
| sed ‘/your/ a Replaced line’ test | Add a new line after a match |
| sed ‘/your/ i Replaced line’ test | Add a new line before a match |
2) Use a different delimiter
sed 's|system|software|' test
Instead of ‘|’ we can also use ‘_’ or ‘@’ as the delimiters. This is mainly used when the search pattern or the replacement string is url.
3) Use & as the replacement string
sed 's/system/& and &' test
Here in the above example ‘&’ represents the replacement string and hence replace ‘system’ with ‘system and system’.
4) Duplicate the replaced line
sed 's/system/software/p' test
The /p(print) flag prints the replaced line twice in the terminal. In this case the lines which are not replaced will be printed only once.
The following command generate the duplicate of each line in this file:
sed 'p' test
5) Print only the replaced lines
sed -n 's/system/software/p' test
Here the -n option suppresses the duplicate of the replaced lines generated by the /p flag.
If we use the option -n alone without /p, then the sed does not print anything.
6) Delete lines
sed '2 d' test
In this case, it deletes the second line from the file ‘test’.
sed '2,$ d' test
Here, it deletes a range of lines i.e, from second line till the last line.
7) Run multiple sed commands
sed -e 's/An/The' -e 's/is/was/' test
In order to run multiple sed commands either we can pipe the output of one sed command to the other or we can use the ‘-e’ option.
8) Sed as grep command
Case 1: cat test An operating system is a vital component of the system. The operating system controls your computer's tasks and system resources to optimize performance. An operating system is a collection of softwares. An operating system is abbreviated as OS. Case 2: sed -n '/vital/ p' test An operating system is a vital component of the system. Case 3: sed -n '/vital/ !p' test The operating system controls your computer's tasks and system resources to optimize performance. An operating system is a collection of softwares. An operating system is abbreviated as OS.
Here in the above example,
Case 1 shows the contents of the file “test”
Case 2 executes sed command to print the lines which match the pattern “vital”. This is same as grep command.
Case 3 executes sed command to print the lined which do not match with the pattern “vital”. This is same as grep -v.
9) Sed as tr command
sed 'y/ATp/atP/' test
The sed command along with y flag acts as tr command. Here in the above example, the sed command use ‘y’ flag to replace ‘A’ with ‘a’ and ‘T’ with ‘t’ which is similar to the action performed by tr command.
10) Edit the source file
sed -i 's/system/software/' test
Sed command by default does not edit the source file for our safety but by using ‘-i’ option source file can be edited.
11) Take backup of source file prior to editing
sed -i.back 's/system/software/' test
In the above sed command, before editing the source file sed command takes the backup of ‘test’ as ‘test.back’.
sed command is case-sensitive. Use /I or /i flag for case-insensitive search.
There are many more examples of sed command. Here I chose these examples to illustrate some basic concepts. This concludes my tutorial on sed and I hope you enjoyed it.
Category : Howtos, Linux

Add new commentSIGN IN